Category Archives: Space Flight
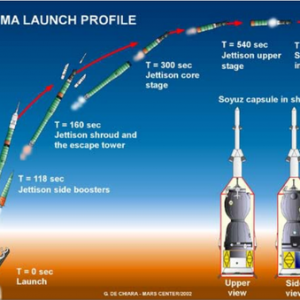
The Most Launched Rocket – History Of The R-7
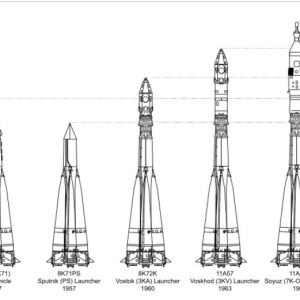
The Most Launched Rocket – History Of The R-7 Continue reading
How does a Soyuz land?

Perhaps the riskiest and scariest part of the Soyuz flight comes at the very end, with the fiery reentry … Continue reading
Powering a Starship With a Black Hole

Powering a Starship With a Black Hole Continue reading
Hybrid Propellants
Rocket Propellants 1) Liquid Propellants 2) Solid Propellants 3) Hybrid Propellants Hybrid propellant engines represent an intermediate group between solid and liquid … Continue reading
Solid Propellants
Rocket Propellants 1) Liquid Propellants 2) Solid Propellants 3) Hybrid Propellants Solid propellant motors are the simplest of all rocket designs. … Continue reading
Liquid Propellants
Rocket Propellants 1) Liquid Propellants 2) Solid Propellants 3) Hybrid Propellants In a liquid propellant rocket, the fuel and oxidizer are stored … Continue reading
Hyperbolic Departure and Approach
Interplanetary flight: 1) Introduction 2) Heliocentric Transfer Orbit 3) The Gauss Problem 4) Determining Orbital Elements 5) Hyperbolic Departure and Approach 6) Gravitational Assist … Continue reading
Determining Orbital Elements
Interplanetary flight: 1) Introduction 2) Heliocentric Transfer Orbit 3) The Gauss Problem 4) Determining Orbital Elements 5) Hyperbolic Departure and Approach 6) Gravitational Assist … Continue reading